The Gulf Cooperation Council’s (GCC) Joint Defence Council held an emergency session in Doha, Qatar, on Thursday, to debate pressing regional safety measures in response to the latest Israeli strike on a Hamas office in Qatar’s capital, which killed six people.
GCC Secretary-Basic Jasem Mohamed AlBudaiwi mentioned the assault on the State of Qatar will be thought-about an assault on all GCC international locations.
Beneficial Tales
record of three objectsfinish of record
AlBudaiwi mentioned member states would activate joint defence mechanisms, improve intelligence sharing, coordinate aerial positions, activate an early-warning system towards ballistic missiles and perform joint coaching workouts, together with a regional air drive drill.
Qatar is the seventh nation Israel has bombed because the begin of this yr.
Which international locations make up the GCC, and what do they spend on their militaries?
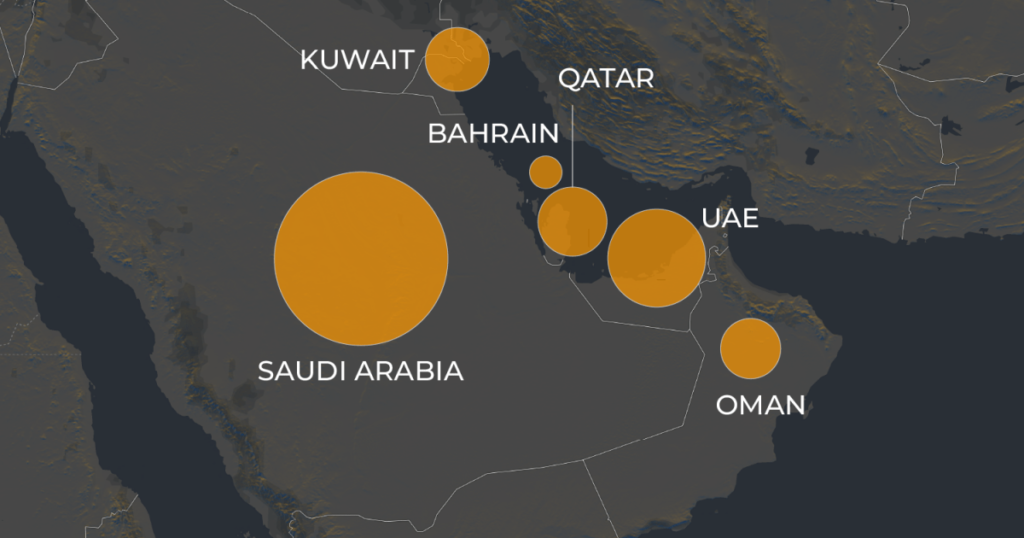
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a political and financial bloc which was shaped in 1981. It brings collectively six Arab states on the Arabian Peninsula:
- Bahrain
- Kuwait
- Oman
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The GCC was established to advertise cooperation on safety, economics and politics, and it typically coordinates positions on regional and worldwide points.
In 2023, GCC international locations collectively spent $114.5bn on their militaries. Saudi Arabia accounted for the most important share, budgeting for at the least $69bn and rating because the world’s seventh-largest army spender, adopted by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at $20.7bn, Qatar at $9.02bn, Kuwait at $7.77bn, Oman at $6.5bn and Bahrain at $1.4bn, based on the Worldwide Institute for Strategic Research, Navy Stability 2024.

The place are the US army bases within the Center East?
The US has operated army bases within the Center East for many years.
Based on the Council on International Relations, the US operates a broad community of army websites, each everlasting and short-term, throughout at the least 19 areas within the area.
Of those, eight are everlasting bases in 5 of the six GCC international locations – Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates – in addition to in Egypt, Iraq and Jordan.

The strategic partnership between Qatar and the US
Al Udeid Air Base was established in Qatar in 1996 and is the most important US army base within the Center East. Masking an space of 24 hectares (60 acres), the bottom accommodates virtually 100 plane in addition to drones. This base, which homes some 10,000 troops, serves because the ahead headquarters for US Central Command (CENTCOM) and has been central to operations in Iraq, Syria and Afghanistan.
Following Israel’s assaults on Doha, US Secretary of State Marco Rubio visited Qatar, arriving the day after he attended meetings in Israel.
Throughout his go to, Qatar’s International Ministry spokesman, Majed al-Ansari, emphasised the nation’s strategic relationship with america, notably on defence issues. He added: “We’re decided to defend our sovereignty and take measures to stop any recurrence of such an assault.”

Saudi-Pakistan defence pact
On Wednesday night, Saudi Arabia signed a “strategic mutual defence settlement” (SMDA) with nuclear-armed Pakistan.
The settlement states that any aggression towards both nation shall be thought-about an act of aggression towards each.
The pact got here simply days after practically 60 member states of the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) gathered in Doha in a present of regional solidarity with Qatar within the wake of the latest assault.

Which air defence programs do Gulf states depend on?
The six Gulf states have constructed layered air defence networks combining US, European, Russian and Chinese language programs.
Their arsenals vary from long-range interceptors to point-defence missiles and anti-aircraft weapons.
Lengthy-range programs cowl threats past 100 km (62 miles), medium-range defend targets 30–100 km (19–62 miles) away and short-range programs defend property inside 1–30 km (0.6–19 miles).

Saudi Arabia possesses the Gulf’s largest air defence community, anchored by US-made THAAD programs and long-range Patriot PAC-3 batteries.
Its layered arsenal additionally contains medium-range US-made I-Hawk missiles, short-range French Crotale, Shahine and MICA programs, in addition to a lot of American and French point-defence launchers equivalent to Stinger, Avenger, Mistral and MPCV. Complementing these are intensive anti-aircraft weapons from a number of international locations, together with the US-made Vulcan, Swiss/German Oerlikon, and Swedish Bofors L/70 fashions.
Saudi Arabia is the one GCC nation to deploy the Chinese language-made Silent Hunter laser system, which tracks and neutralises low-flying drones and different small aerial threats by emitting a high-energy beam that may disable or destroy them.

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) operates US-made THAAD and long-range Patriot programs, alongside a model of the Israeli-made Barak air defence system.
For medium-range threats, the UAE depends on the South Korean-made Cheongung II.
Its short-range defences embrace French Crotale and Mistral, Russian Igla and Pantsir-S1, Swedish RBS-70 and British Rapier programs, all supported by a wide range of European anti-aircraft weapons.
Saudi Arabia and the UAE are the one two GCC international locations which function the THAAD (Terminal Excessive Altitude Space Defence) system, giving them superior missile interception capabilities towards ballistic threats.

Qatar has invested in US-made Patriot programs and NASAMS III for long- and medium-range air defence, whereas its short-range defences characteristic a mixture of Russian Igla, US Stinger, Chinese language FN-6 and French Mistral programs, supported by German Gepard and Skynex anti-aircraft weapons.
Kuwait fields US-made Patriot PAC-3 batteries for long-range defence, Italian Aspide launchers paired with Skyguard programs for short-range defence and Stinger, Starburst and FIM-92 missiles for level defence, complemented by German Oerlikon GDF anti-aircraft weapons.
Bahrain has lately acquired the Patriot PAC-3 MSE system, becoming a member of Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Qatar and Kuwait because the GCC international locations with superior long-range, surface-to-air missile capabilities.
For medium- to short-range threats, it depends on US I-Hawk and French Crotale programs, supported by Russian Igla, US Stinger and Swedish RBS-70 point-defence missiles, in addition to Oerlikon anti-aircraft weapons.
Oman lacks superior long- and medium-range missile programs in contrast with different GCC international locations. Its short-range programs embrace the Norwegian-US-made NASAMS, complemented by French Mistral, US Javelin and Russian Strela-2 point-defence missiles, backed by Russian, Swiss and Swedish gun programs.