IEEE Spectrum’s hottest biomedical tales of the final yr centered each on incorporating new applied sciences and revamping outdated ones. Whereas AI is all the trend in most sectors—together with biomed, with purposes like an in-brain warning system for worsening mental health and a mannequin to estimate heart rate in actual time—biomedical information this previous yr has additionally centered on legacy applied sciences. Tech like Wi-Fi, ultrasound, and lasers have all made comebacks or discovered new makes use of in 2025.
Whether or not innovation stems from new tech or outdated, IEEE Spectrum will proceed to cowl it rigorously in 2026.
Georgia Institute of Technology, Icahn Faculty of Medication at Mt. Sinai and TeraPixel
When Patricio Riva Posse, a psychiatrist at Emory College Faculty of Medication, realized that his affected person’s brain implants have been sending him indicators about her worsening despair earlier than she even acknowledged something was flawed, he wished he might have taken motion sooner.
That have led him and colleagues to develop “an automated alarm system” for indicators of adjusting psychological well being. The software screens mind indicators in actual time, utilizing implants to report electrical impulses, and AI to research the outputs and flag warning indicators of relapse. Different analysis teams throughout the United States are experimenting with alternative ways to make use of these stimulating mind implants to assist deal with despair, each with and with out the assistance of AI. “There are such a lot of levers we will press right here,” neurosurgeon Nir Lipsman says within the article.
 Dmitry Kireev/College of Massachusetts Amherst
Dmitry Kireev/College of Massachusetts Amherst
In Dmitry Kireev’s lab on the College of Massachusetts Amherst, researchers are creating imperceptibly skinny graphene tattoos able to monitoring your vital signs and extra. “Digital tattoos might assist folks observe advanced medical situations, together with cardiovascular, metabolic, immune system, and neurodegenerative ailments. Almost half of U.S. adults could also be within the early levels of a number of of those problems proper now, though they don’t but understand it,” he wrote in an article for IEEE Spectrum.
How does it work? Graphene is conductive, sturdy, and versatile, in a position to measure options like coronary heart charge and the presence of sure compounds in sweat. For now, the tattoos should be plugged into an everyday digital circuit, however Kireev hopes that they may quickly be built-in into smartwatches, and thus less complicated to put on.
 Erika Cardema/UC Santa Cruz
Erika Cardema/UC Santa Cruz
Wi-Fi can do extra than simply get you linked to the web—it might probably assist monitor your coronary heart inexpensively and with out requiring fixed bodily contact. The brand new method, known as Pulse-Fi, makes use of an AI mannequin to research heartbeats to estimate coronary heart charge in actual time from as much as 10 ft away.
The system is low value, totaling round US $40, simple to deploy, and doesn’t introduce discomfort. It additionally works whatever the consumer’s posture and in every kind of environments. Katia Obraczka, a pc scientist on the College of California, Santa Cruz who led the event of Pulse-Fi, says the staff plans to commercialize the expertise.
 Shonagh Rae
Shonagh Rae
Sangeeta S. Chavan and Stavros Zanos, biomedical researchers on the Institute of Bioelectronic Medicine in New York, hypothesize that ultrasound waves could activate neurons, providing “a exact and secure means to supply therapeutic therapies for a variety of each acute and continual maladies,” as they write in an article for Spectrum. Focused ultrasound might then function a therapy for irritation or diabetes, as a substitute of remedy with wide-ranging negative effects, they are saying.
It really works by vibrating a neuron’s membrane and “opening channels that permit ions to circulate into the cell, thus not directly altering the cell’s voltage and inflicting it to fireplace,” they write. The authors suppose that activating particular neurons can assist handle the foundation causes of particular diseases.
 Excessive Mild group/College of Glasgow
Excessive Mild group/College of Glasgow
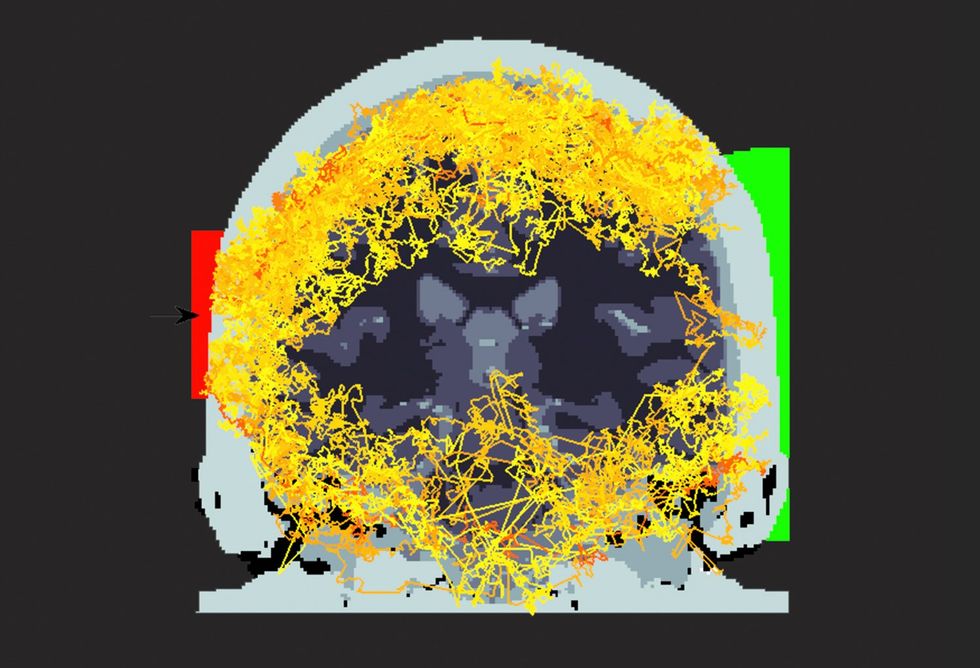
If a physician needs to see inside your head, they must resolve whether or not they need to achieve this cheaply or deeply—an electroencephalograph is cheap, however doesn’t penetrate previous the outer layers of the mind, whereas functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is dear, however can see all the best way in. Shining a laser by way of an individual’s head looks as if step one in the direction of expertise that accomplishes each.
For a few years, this sort of work has appeared not possible as a result of the human head is so good at blocking mild, however researchers have now confirmed that lasers can ship photons all through. “What was thought not possible, we’ve proven to be potential. And hopefully…that might encourage the following era of those units,” undertaking lead Jack Radford says within the article.
 Jiawei Ge
Jiawei Ge
Within the not-to-distant future, surgical sufferers could hear “The robotic will see you now,” because the authors of this story counsel. The three researchers work on the Johns Hopkins University robotics lab accountable for creating Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR), which carried out the primary autonomous soft-tissue surgery in a dwell animal in 2016.
Whereas there are definitely challenges remaining within the quest to deliver autonomous robots into the working room—like creating basic objective robotic controllers and gathering information inside strict privateness rules—the tip aim is on the horizon. “A state of affairs through which sufferers are routinely greeted by a surgeon and an autonomous robotic assistant is not a distant chance,” the authors write.
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet
